In this course we will discuss dementia. We will explain how dementia affects the brain. We will discuss how Alzheimer’s disease differs from other types of dementia. We will go over behaviors you will see every day in people with mild, moderate, and severe dementia. Finally, we will discuss communication issues you might see at different stages of dementia.
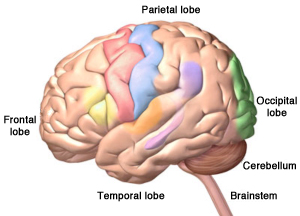
Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia are caused by damage to the brain. The part of the brain that is damaged in dementia is called the cerebrum. The cerebrum fills up most of our skull and is divided into four lobes:
- Frontal lobes: reasoning, judgement, motor control, planning, decision-making
- Temporal lobes: memory and emotion, hearing, language
- Parietal lobes: sensation, touch, temperature, pressure, pain
- Occipital lobes: visual processing, depth, distance, location of objects
The cerebrum is what makes us human—it does our thinking, remembering, talking, and understanding. It controls our emotions. It helps us reason things out and make decisions. It helps us tell right from wrong. It also controls our movements, vision, and hearing. Many of these areas of the cerebrum are damaged by dementia.
The Human Brain
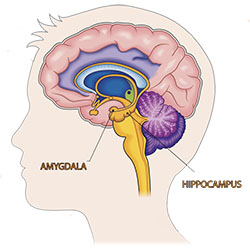
The hippocampus is involved with creation of short term memories. The amygdala is involved with emotional control.
The four lobes of the cerebrum, plus the cerebellum and the brainstem. Alzheimer’s disease starts in the temporal lobe in an area called the hippocampus. Left: Copyright, Zygote Media Group, Inc. Used with permission. Right: National Institutes of Health, Credit: iStock/jambojam. Public domain. From: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/news/science-news/2019/study-reveals-sex-based-differences-in-the-development-of-brain-hubs-involved-in-memory-and-emotion.shtml.
Our brain has two other important parts: the cerebellum and the brainstem. Touch the back of your head just above your neck. The cerebellum is right there. It controls coordination and balance.
Cerebellum and Brainstem
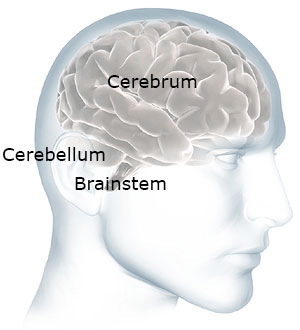
The cerebellum and brainstem are at the back of your head, below the cerebrum.
Now move your hand a little down and stop before your get to your spine. The brainstem is right there—at the back of the head, above your spine. It connects the brain to the spinal cord. The brainstem oversees automatic things like breathing, digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure. The cerebellum and the brainstem are usually not affected by dementia.
What Is Dementia?
Dementia is a brain disease. It is progressive, meaning it gets worse over time. It is a terminal illness, meaning it will eventually lead to death. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common kind of dementia.
AD begins in the area of the brain that makes new memories, called the hippocampus. The hippocampus is the memory center of the brain, responsible for forming short-term memories. That’s why someone with AD forgets something that happened just a moment ago. This part of the brain also helps us associate memories with various senses, such as smell.
Other types of dementia begin in areas of the brain involved with thinking and reasoning. Although dementia can start in one part of the brain, eventually it will affect the entire brain.
Emotions are also affected when someone gets dementia. That’s why someone with Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia sometimes has difficulty controlling their emotions.
When someone has dementia, their thinking becomes less clear. Decisions are more difficult and safety awareness declines. People also tire more easily. Eventually, people with dementia lose the ability to take care of themselves. In the end, they may also lose their appetite and stop eating.
For people between the ages of 65 and 75, only about 5% will get any sort of dementia. For people over the age of 85, about 40% will experience some form of dementia. Even so, dementia is not considered a normal part of aging.
How Does Dementia Affect the Brain?
Dementia changes the entire brain. In Alzheimer’s disease, nerve cells in the brain are damaged by something called plaques and tangles. As the nerve cells die, the brain gets smaller. Over time, the brain shrinks, affecting nearly all its functions.
Normal Brain Contrasted with AD Brain
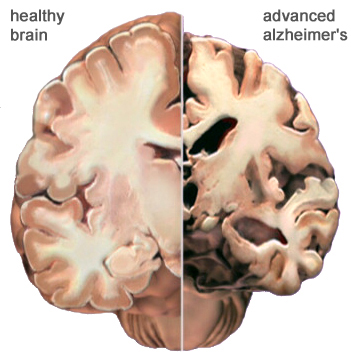
A view of how Alzheimer’s disease changes the whole brain. Left side: normal brain; right side, a brain damaged by advanced AD. Source: Courtesy of The Alzheimer’s Association. Used with permission.
In Alzheimer’s disease, damage begins in the temporal lobe, in and around the hippocampus. The hippocampus a part of the brain that is responsible for new memories, spatial awareness, and control of emotions.
Dementia affects what are called executive functions: mental skills that include memory, thinking, and self-control. We use these skills to manage daily life. Dementia causes a gradual loss of executive functions and makes it hard to plan for the future, follow complex conversations, remember new things, and control emotions.
As the disease progresses, plaques and tangles spread to the front part of the brain (the temporal and frontal lobes). These areas of the brain are involved with language, judgment, and learning. Speaking and understanding speech, the sense of where your body is in space, and executive functions such as planning and ethical thinking are affected.
In severe Alzheimer’s disease, damage is spread throughout the brain. At this stage, because so many areas of the brain are affected, individuals lose the ability to communicate, to recognize family and loved ones, and to care for themselves.
Normal Age-Related Changes
We all experience changes as we age. Some people become forgetful when they get older. They may forget where they left their keys. They may also take longer to do certain mental tasks. They may not think as quickly as they did when they were younger. These are called age-related changes. This is a normal part of aging—it not dementia.
Age-related changes don’t affect a person’s life very much. Someone with age-related changes can easily do everything in their daily lives—they can prepare their own meals, manage their finances, safely drive a car, go shopping, and use a computer. They understand when they are in danger. They know how to take care of themselves. Even though they might not think or move as fast as when they were young, their thinking is normal—they do not have dementia.
The table below describes some of the differences between someone who is aging normally and someone who has some form of dementia.
Normal Aging vs. ADRD | |
|---|---|
Normal aging | AD or other dementia |
Occasionally loses keys | Cannot remember what a key does |
May not remember names of people they meet | Cannot remember names of spouse and children—don’t remember meeting new people |
May get lost driving in a new city | Get lost in own home, forget where they live |
Can use logic (for example, if it is dark outside it is night time) | Is not logical (if it is dark outside it could be morning or evening) |
Dresses, bathes, feeds self | Cannot remember how to fasten a button, operate appliances, or cook meals |
Participates in community activities such as driving, shopping, exercising, and traveling | Cannot independently participate in community activities, shop, or drive |
In some older adults, memory problems are a little bit worse than normal age-related changes. This is known as mild cognitive impairment, also called MCI.
Mild cognitive impairment isn’t dementia although you may see personality changes, as well as a little more difficulty than is normal with thinking and memory. For some people, mild cognitive impairment gets worse and develops into dementia, but this doesn’t happen with everyone.
Changes in behavior can occur in older adults and may be a risk factor for dementia. This is called mild behavioral impairment or MBI. Signs of MBI are apathy, mood swings, anxiety, agitation and aggression, social withdrawal, and abnormal thoughts (Matsuoka, 2019).
What Is Alzheimer’s Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia. Nearly 6 million people in the United States suffer from Alzheimer’s. It is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States and affects women more than men. About two-thirds of Americans caring for someone with Alzheimer’s disease are women (Alzheimer’s Association, 2019).
The first thing you will notice in someone with Alzheimer’s disease is that they have trouble making new memories. This is called short-term memory loss. This happens because the part of the brain where new memories are formed becomes damaged by dementia.
Long-ago memories are stored in a part of the brain that is not affected by Alzheimer’s dementia. Especially at first, people can remember and talk about events from earlier times in their lives. As the dementia gets worse and more of the brain is affected, long ago memories might also start to fade.
